X
Код презентации скопируйте его
Метод учебных проектов как средство активизации учебной деятельности на уроках английского языка
Скачать эту презентациюПрезентация на тему Метод учебных проектов как средство активизации учебной деятельности на уроках английского языка
Скачать эту презентациюCлайд 1
 МЕТОД УЧЕБНЫХ ПРОЕКТОВ КАК СРЕДСТВО АКТИВИЗАЦИИ УЧЕБНОЙ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ НА УРОКАХ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА Учитель английского языка МОУ СОШ №288 Самсонова Наталья Владимировна
МЕТОД УЧЕБНЫХ ПРОЕКТОВ КАК СРЕДСТВО АКТИВИЗАЦИИ УЧЕБНОЙ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ НА УРОКАХ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА Учитель английского языка МОУ СОШ №288 Самсонова Наталья Владимировна
Cлайд 2
 Определение понятия Метод проектов – система обучения, при которой учащиеся приобретают знания в процессе планирования и выполнения постоянно усложняющихся практических заданий – проектов.
Определение понятия Метод проектов – система обучения, при которой учащиеся приобретают знания в процессе планирования и выполнения постоянно усложняющихся практических заданий – проектов.
Cлайд 3
 Главная особенность Главная особенность метода – обучение на активной основе, через целесообразную деятельность ученика, соответствующую его личным интересам. Основоположник – Джон Дьюи (США) 1859-1952
Главная особенность Главная особенность метода – обучение на активной основе, через целесообразную деятельность ученика, соответствующую его личным интересам. Основоположник – Джон Дьюи (США) 1859-1952
Cлайд 4
 Метод проектов в России 1905 – начало проектных технологий под руководством С.Т. Шацкого 20-е годы – внедрение «комплексного метода», серия ошибок и перегибов. 1931 год – запрет на применение метода проектов 90-е годы XX века – возрастание интереса, становится неотъемлемой частью концепции модернизации российского образования.
Метод проектов в России 1905 – начало проектных технологий под руководством С.Т. Шацкого 20-е годы – внедрение «комплексного метода», серия ошибок и перегибов. 1931 год – запрет на применение метода проектов 90-е годы XX века – возрастание интереса, становится неотъемлемой частью концепции модернизации российского образования.
Cлайд 5
 Достоинства проектной деятельности Развивает способности · к осмыслению своей деятельности с позиций ценностного подхода; · к целеполаганию; · к самообразованию и самоорганизации; · к синтезированию, интеграции и обобщению информации из разных источников; · к творчеству · делать выбор и принимать решения.
Достоинства проектной деятельности Развивает способности · к осмыслению своей деятельности с позиций ценностного подхода; · к целеполаганию; · к самообразованию и самоорганизации; · к синтезированию, интеграции и обобщению информации из разных источников; · к творчеству · делать выбор и принимать решения.
Cлайд 6
 Этапы работы над учебным проектом Проблема проекта Почему? Актуальность проблемы Цель проекта Зачем? Целеполагание Задачи проекта Что? Постановка задач Методы и способы Как? Планирование Результат Что получится? Ожидаемый результат
Этапы работы над учебным проектом Проблема проекта Почему? Актуальность проблемы Цель проекта Зачем? Целеполагание Задачи проекта Что? Постановка задач Методы и способы Как? Планирование Результат Что получится? Ожидаемый результат
Cлайд 7
 Виды проектов на уроках английского языка Индивидуальный письменный Коллективный (или парный) письменный Коллективный (или парный) устный
Виды проектов на уроках английского языка Индивидуальный письменный Коллективный (или парный) письменный Коллективный (или парный) устный
Cлайд 8
 Формы индивидуального и коллективного (письменного проектов) проектов Описание ( дома, школы будущего .достопримечательности и т. д.) Рассказ ( сказка, детектив) Рецензия на книгу Мини-исследование об истории вещей Сценарий к фильму Коллаж из нескольких текстов на заданную тему и др. Компьютерная презентация Художественный перевод стихотворения
Формы индивидуального и коллективного (письменного проектов) проектов Описание ( дома, школы будущего .достопримечательности и т. д.) Рассказ ( сказка, детектив) Рецензия на книгу Мини-исследование об истории вещей Сценарий к фильму Коллаж из нескольких текстов на заданную тему и др. Компьютерная презентация Художественный перевод стихотворения
Cлайд 22
 For nearly 200 years Tzarskoje Selo had been a summer residence of the Russian Royal Family. Many of the significant state affairs were conducted here. The magnificence of its fronts, interieur, pavilions and parks putsTzarskoje Selo into the rank of the world's largest museums. The real gem of the Catherine palace, the Amber room, is considered the eighth wonder of the world.
For nearly 200 years Tzarskoje Selo had been a summer residence of the Russian Royal Family. Many of the significant state affairs were conducted here. The magnificence of its fronts, interieur, pavilions and parks putsTzarskoje Selo into the rank of the world's largest museums. The real gem of the Catherine palace, the Amber room, is considered the eighth wonder of the world.
Cлайд 23
 EMPEROR PETR I Petr I Alexeevich (1672-1725) - Tsar from 1682, Emperor from 1721. EMPRESS CATHERINE I Catherine I Alexeevna (1684 -1727) - Empress from 1725 EMPEROR PETR II Petr II Alexeevich (1715-1730) - Emperor from 1727. EMPRESS ANNA IVANOVNA Anna Ivanovna (1693-1740) - Empress from 1730. EMPEROR IVAN VI Ivan VI Antonovich (1740-1764) - Emperor from 1740 to 1741. EMPRESS ELIZABETH I Elizabeth Petrovna (1709-1761) - Empress from 1741 EMPEROR PETR III Petr III Fyodorovich (1728 - 1762) - Emperor from 1761 to 1762 EMPRESS CATHERINE II Catherine II Alexeevna (1729-1796) - Empress from 1762.
EMPEROR PETR I Petr I Alexeevich (1672-1725) - Tsar from 1682, Emperor from 1721. EMPRESS CATHERINE I Catherine I Alexeevna (1684 -1727) - Empress from 1725 EMPEROR PETR II Petr II Alexeevich (1715-1730) - Emperor from 1727. EMPRESS ANNA IVANOVNA Anna Ivanovna (1693-1740) - Empress from 1730. EMPEROR IVAN VI Ivan VI Antonovich (1740-1764) - Emperor from 1740 to 1741. EMPRESS ELIZABETH I Elizabeth Petrovna (1709-1761) - Empress from 1741 EMPEROR PETR III Petr III Fyodorovich (1728 - 1762) - Emperor from 1761 to 1762 EMPRESS CATHERINE II Catherine II Alexeevna (1729-1796) - Empress from 1762.
Cлайд 24
 EMPEROR PAUL I Paul I Petrovich (1754-1801) - Emperor from 1796. EMPEROR ALEXANDER I Alexander I Pavlovich (1777-1825) - Emperor from 1801 EMPEROR NICHOLAS I Nicholas I Pavlovich (1796-1855) - Emperor from 1825. EMPEROR ALEXANDER II Alexander II Nikolaevich (1818-1881) - Emperor from 1855. EMPEROR ALEXANDER III Alexander III Alexandrovich (1845-1894) - Emperor from 1881. EMPEROR Nicholas II Nicholas II Alexandrovich (1868-1918) - last Russian emperor, ruled from 1894 to 1917
EMPEROR PAUL I Paul I Petrovich (1754-1801) - Emperor from 1796. EMPEROR ALEXANDER I Alexander I Pavlovich (1777-1825) - Emperor from 1801 EMPEROR NICHOLAS I Nicholas I Pavlovich (1796-1855) - Emperor from 1825. EMPEROR ALEXANDER II Alexander II Nikolaevich (1818-1881) - Emperor from 1855. EMPEROR ALEXANDER III Alexander III Alexandrovich (1845-1894) - Emperor from 1881. EMPEROR Nicholas II Nicholas II Alexandrovich (1868-1918) - last Russian emperor, ruled from 1894 to 1917
Cлайд 25
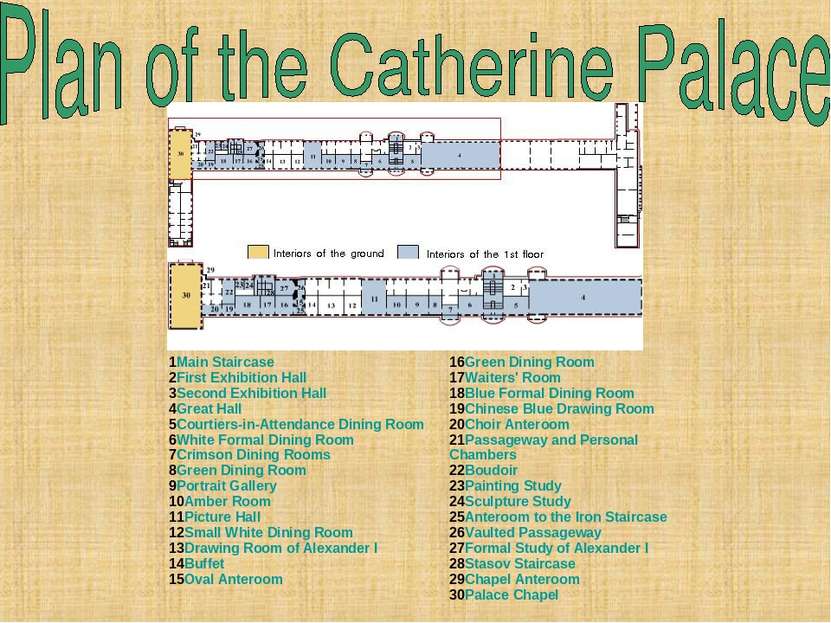
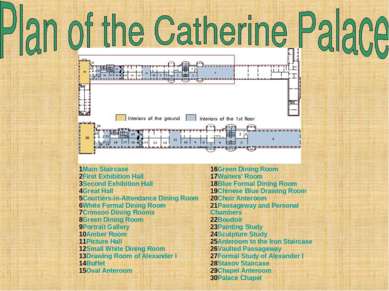 1Main Staircase 2First Exhibition Hall 3Second Exhibition Hall 4Great Hall 5Courtiers-in-Attendance Dining Room 6White Formal Dining Room 7Crimson Dining Rooms 8Green Dining Room 9Portrait Gallery 10Amber Room 11Picture Hall 12Small White Dining Room 13Drawing Room of Alexander I 14Buffet 15Oval Anteroom 16Green Dining Room 17Waiters' Room 18Blue Formal Dining Room 19Chinese Blue Drawing Room 20Choir Anteroom 21Passageway and Personal Chambers 22Boudoir 23Painting Study 24Sculpture Study 25Anteroom to the Iron Staircase 26Vaulted Passageway 27Formal Study of Alexander I 28Stasov Staircase 29Chapel Anteroom 30Palace Chapel
1Main Staircase 2First Exhibition Hall 3Second Exhibition Hall 4Great Hall 5Courtiers-in-Attendance Dining Room 6White Formal Dining Room 7Crimson Dining Rooms 8Green Dining Room 9Portrait Gallery 10Amber Room 11Picture Hall 12Small White Dining Room 13Drawing Room of Alexander I 14Buffet 15Oval Anteroom 16Green Dining Room 17Waiters' Room 18Blue Formal Dining Room 19Chinese Blue Drawing Room 20Choir Anteroom 21Passageway and Personal Chambers 22Boudoir 23Painting Study 24Sculpture Study 25Anteroom to the Iron Staircase 26Vaulted Passageway 27Formal Study of Alexander I 28Stasov Staircase 29Chapel Anteroom 30Palace Chapel
Cлайд 26
 The exposition in the Catherine Palace Museum (prior to 1910 - the Great Tzarskoje Selo Palace) encompasses the 250-year history of the famous monument, and acquaints visitors with the work of the architects who participated in its construction and decoration in the 18th and 19th centuries, and also with the current state of this unique landmark, with the work of restorers who managed to bring the palace back to life after World War II. The Tzarskoje Selo and the Orient exposition, located in the former personal quarters not yet restored, continues to be featured at the Catherine Palace Museum.
The exposition in the Catherine Palace Museum (prior to 1910 - the Great Tzarskoje Selo Palace) encompasses the 250-year history of the famous monument, and acquaints visitors with the work of the architects who participated in its construction and decoration in the 18th and 19th centuries, and also with the current state of this unique landmark, with the work of restorers who managed to bring the palace back to life after World War II. The Tzarskoje Selo and the Orient exposition, located in the former personal quarters not yet restored, continues to be featured at the Catherine Palace Museum.
Cлайд 27
 Between the years 1752 and 1756, during reconstruction of the Catherine Palace, Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli placed the Main Staircase at a distance from the entrance gates to the palace in the southern part of the building, topped by a spired dome. Rastrelli's Main Staircase was destroyed at the end of the 18th century during the reign of Catherine II. In its place, Charles Cameron erected a new Main Staircase in the center of the palace, in place of the Chinese Hall created by Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli. The staircase occupies the entire height and width of the Catherine Palace and is illuminated from the east and west by windows placed on three levels. The walls boast decorative 18th and 19th century Chinese and Japanese porcelain vases and plates. The windows of the Main Staircase are dressed with crimson draperies.
Between the years 1752 and 1756, during reconstruction of the Catherine Palace, Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli placed the Main Staircase at a distance from the entrance gates to the palace in the southern part of the building, topped by a spired dome. Rastrelli's Main Staircase was destroyed at the end of the 18th century during the reign of Catherine II. In its place, Charles Cameron erected a new Main Staircase in the center of the palace, in place of the Chinese Hall created by Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli. The staircase occupies the entire height and width of the Catherine Palace and is illuminated from the east and west by windows placed on three levels. The walls boast decorative 18th and 19th century Chinese and Japanese porcelain vases and plates. The windows of the Main Staircase are dressed with crimson draperies.
Cлайд 28
 The First Exhibition Hall can be reached from the Main Staircase of the Catherine Palace. The exposition in this room acquaints visitors with the main stages in the creation of the Catherine Palace. In the center of the left wall, among antique engravings, can be seen the communique from P. Apraxin to Emperor Peter I dated August 24, 1702, in which Sarskaya myza, which would later become Tzarskoje Selo, is mentioned for the first time. Hanging next to this is the drawing "Sixteen Stone Chambers" depicting the first Tzarskoje Selo palace, designed by Johann Friedrich Braunstein. The Second Exhibition Hall The Second Exhibition Hall is located next to the First Exhibition Hall. The exposition in this room tells of the tragic events connected with the years of World War II in Tzarskoje Selo. It also covers the evacuation of the museum's treasures from the Catherine and Alexander Palaces organized by the Soviet government, during which approximately 70,000 objects were rescued
The First Exhibition Hall can be reached from the Main Staircase of the Catherine Palace. The exposition in this room acquaints visitors with the main stages in the creation of the Catherine Palace. In the center of the left wall, among antique engravings, can be seen the communique from P. Apraxin to Emperor Peter I dated August 24, 1702, in which Sarskaya myza, which would later become Tzarskoje Selo, is mentioned for the first time. Hanging next to this is the drawing "Sixteen Stone Chambers" depicting the first Tzarskoje Selo palace, designed by Johann Friedrich Braunstein. The Second Exhibition Hall The Second Exhibition Hall is located next to the First Exhibition Hall. The exposition in this room tells of the tragic events connected with the years of World War II in Tzarskoje Selo. It also covers the evacuation of the museum's treasures from the Catherine and Alexander Palaces organized by the Soviet government, during which approximately 70,000 objects were rescued
Cлайд 29
 The Great Hall, or the Light Gallery, as it was called in the 18th century, is a formal apartment in the Russian baroque style designed by the architect Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli between 1752 and 1756. The Great Hall was intended for more significant receptions and celebrations, including formal dinners, balls and masquerades. The hall is painted in two colors, with an area of approximately 1,000 square meters, and occupies the entire width of the palace. The windows on the eastern side look out onto the park, and on the western side, onto the palace square. In the summer, the hall is penetrated by sunlight which plays on the gilding throughout the day, and in the evening 696 lamps are lit on 12 - 15 chandeliers located near the mirrors, which made the impression of the hall more effective.
The Great Hall, or the Light Gallery, as it was called in the 18th century, is a formal apartment in the Russian baroque style designed by the architect Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli between 1752 and 1756. The Great Hall was intended for more significant receptions and celebrations, including formal dinners, balls and masquerades. The hall is painted in two colors, with an area of approximately 1,000 square meters, and occupies the entire width of the palace. The windows on the eastern side look out onto the park, and on the western side, onto the palace square. In the summer, the hall is penetrated by sunlight which plays on the gilding throughout the day, and in the evening 696 lamps are lit on 12 - 15 chandeliers located near the mirrors, which made the impression of the hall more effective.
Cлайд 30
 If the Amber Room had not disappeared during World War II, we would celebrate its tercentenary in 2001. Prussian kings and Russian emperors, architects and artists, leaders of the Third Reich and Soviet leaders, Maecenases and businessmen, treasure hunters and outstanding scientists, not to mention craftsmen, were involved in the history of the "Eighth Wonder of the World". Today, the theme of reconstruction of the Amber Room is of primary importance. Preserved photographs and archives help the roughly 40 art experts to fashion the barely palm-sized thin amber pieces so that they match the original in shape in colour and to carve fine ornaments, thus recreating the legendary work of art like a huge puzzle from over half a million pieces of amber. The time approaches when, before our very eyes, we will see a replica which looks very much like original, but is a new work of applied art, worthy of being on display in one of the best palace-museums of the world: the Catherine Palace Tzarskoje Selo .
If the Amber Room had not disappeared during World War II, we would celebrate its tercentenary in 2001. Prussian kings and Russian emperors, architects and artists, leaders of the Third Reich and Soviet leaders, Maecenases and businessmen, treasure hunters and outstanding scientists, not to mention craftsmen, were involved in the history of the "Eighth Wonder of the World". Today, the theme of reconstruction of the Amber Room is of primary importance. Preserved photographs and archives help the roughly 40 art experts to fashion the barely palm-sized thin amber pieces so that they match the original in shape in colour and to carve fine ornaments, thus recreating the legendary work of art like a huge puzzle from over half a million pieces of amber. The time approaches when, before our very eyes, we will see a replica which looks very much like original, but is a new work of applied art, worthy of being on display in one of the best palace-museums of the world: the Catherine Palace Tzarskoje Selo .
Cлайд 31
 The Picture Hall is one of the formal rooms in the Catherine Palace, and was designed by Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli in the 1750s. This formal hall occupies approximately 180 square meters, and stretches across the width of the palace. During the 18th century, it was frequently used for diplomatic receptions, meals and music concerts. Meetings, or "conferences at the high court," were also held here during the Seven-year war, (1756-1763) and the summer of 1757 saw a triumphant reception to celebrate the delivery of banners and keys to captured Prussian towns.
The Picture Hall is one of the formal rooms in the Catherine Palace, and was designed by Bartolomeo Francesco Rastrelli in the 1750s. This formal hall occupies approximately 180 square meters, and stretches across the width of the palace. During the 18th century, it was frequently used for diplomatic receptions, meals and music concerts. Meetings, or "conferences at the high court," were also held here during the Seven-year war, (1756-1763) and the summer of 1757 saw a triumphant reception to celebrate the delivery of banners and keys to captured Prussian towns.
Cлайд 32
 From the Room Leading to the Iron Staircase (buffet) one passes into the Waiters' Room. This room was one of the service rooms in the Catherine Palace, hence the name. According to plans by Charles Cameron, it was divided by a cross-wise screen into two "foyers," one of which was dark and led to the staircase. The architectural style was of the classical period. The interior of the Waiters' Room suffered greatly during the fire in 1820. The interior composition created by the architect Charles Cameron with its double pilasters on the walls and broad frieze with archivolts was reproduced with a few changes by the architect Vasily Stasov. Due to the absence оf original drawings of the detail executed by Charles Cameron, the design was modeled after sketches by Vasily Stasov.
From the Room Leading to the Iron Staircase (buffet) one passes into the Waiters' Room. This room was one of the service rooms in the Catherine Palace, hence the name. According to plans by Charles Cameron, it was divided by a cross-wise screen into two "foyers," one of which was dark and led to the staircase. The architectural style was of the classical period. The interior of the Waiters' Room suffered greatly during the fire in 1820. The interior composition created by the architect Charles Cameron with its double pilasters on the walls and broad frieze with archivolts was reproduced with a few changes by the architect Vasily Stasov. Due to the absence оf original drawings of the detail executed by Charles Cameron, the design was modeled after sketches by Vasily Stasov.
Презентации этого автора
Похожие презентаци
 19.06.2014
скрыт
19.06.2014
скрыт