X
Код презентации скопируйте его
The Unique Australian Wildlife
Скачать эту презентациюПрезентация на тему The Unique Australian Wildlife
Скачать эту презентациюCлайд 1
 The Unique Australian Wildlife The notes to the geological history of the continent By Maria Skochilova School 7 Nizhny Tagil
The Unique Australian Wildlife The notes to the geological history of the continent By Maria Skochilova School 7 Nizhny Tagil
Cлайд 3
 320-270 million years ago Permo-Carboniferous Age If we had observed the Earth surface from space at that time, we would have seen quite the other picture
320-270 million years ago Permo-Carboniferous Age If we had observed the Earth surface from space at that time, we would have seen quite the other picture
Cлайд 4
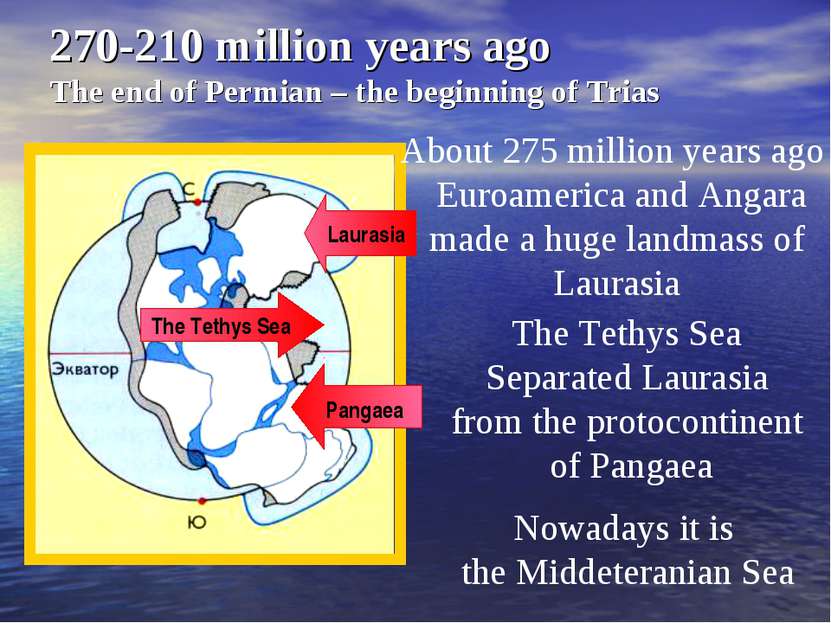
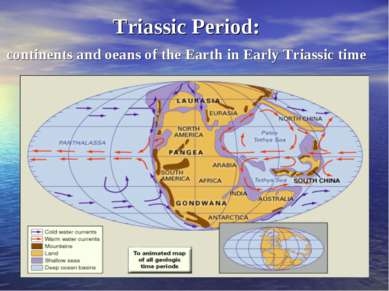
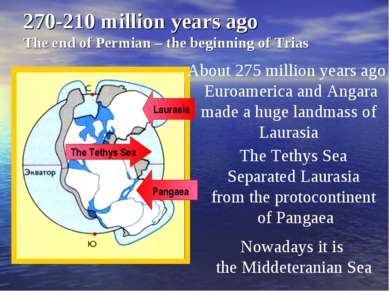 270-210 million years ago The end of Permian – the beginning of Trias About 275 million years ago Euroamerica and Angara made a huge landmass of Laurasia Laurasia The Tethys Sea Separated Laurasia from the protocontinent of Pangaea Pangaea The Tethys Sea Nowadays it is the Middeteranian Sea
270-210 million years ago The end of Permian – the beginning of Trias About 275 million years ago Euroamerica and Angara made a huge landmass of Laurasia Laurasia The Tethys Sea Separated Laurasia from the protocontinent of Pangaea Pangaea The Tethys Sea Nowadays it is the Middeteranian Sea
Cлайд 5
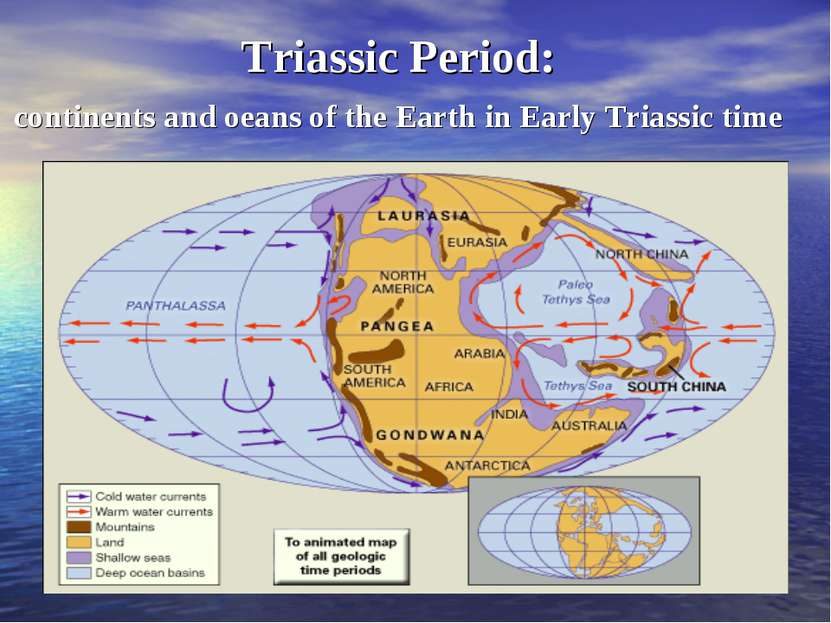
 270-210 million years ago The end of Permian – the beginning of Trias On land the vertebrates are represented in the Triassic by amphibians and reptiles. The first true mammals, which were very small, are supposed to appear in the Late Triassic.
270-210 million years ago The end of Permian – the beginning of Trias On land the vertebrates are represented in the Triassic by amphibians and reptiles. The first true mammals, which were very small, are supposed to appear in the Late Triassic.
Cлайд 7
 Monotreme The egg-laying mammalians include the amphibious platypus and the terrestrial echidnas of Australia, Tasmania, and New Guinea short-beaked echidna amphibious platipus
Monotreme The egg-laying mammalians include the amphibious platypus and the terrestrial echidnas of Australia, Tasmania, and New Guinea short-beaked echidna amphibious platipus
Cлайд 8
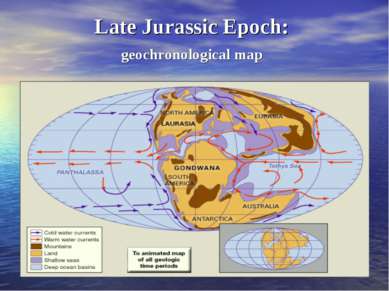
 180 million years ago Middle Jurassic period The protocontinent supposedly covered about half the Earth and was completely surrounded by a world ocean called Panthalassa.
180 million years ago Middle Jurassic period The protocontinent supposedly covered about half the Earth and was completely surrounded by a world ocean called Panthalassa.
Cлайд 9
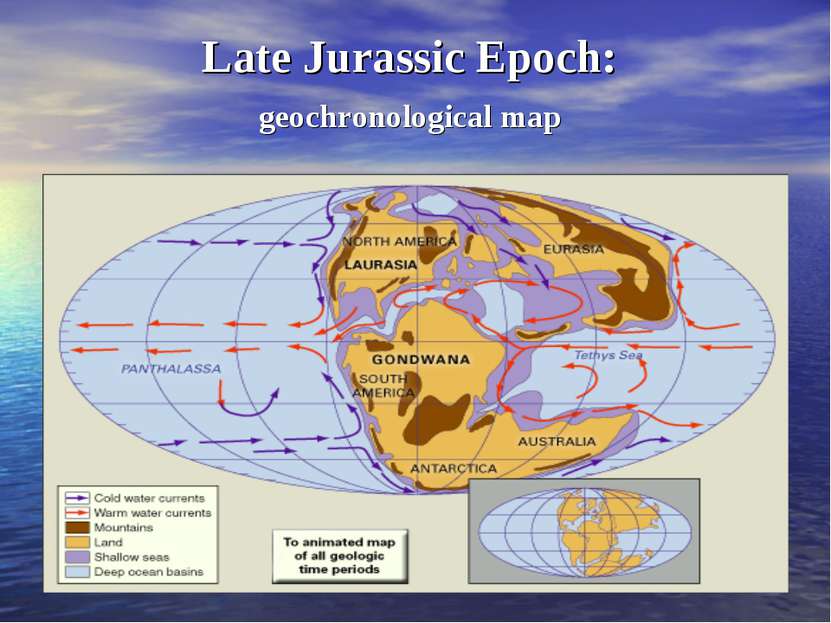
 180 million years ago Middle Jurassic period Dinosaurs and other reptiles emerged to dominate the land, sea, and sky. The first birds and new varieties of reefbuilding and other invertebrate faunas, provided Jurassic life with added complexity.
180 million years ago Middle Jurassic period Dinosaurs and other reptiles emerged to dominate the land, sea, and sky. The first birds and new varieties of reefbuilding and other invertebrate faunas, provided Jurassic life with added complexity.
Cлайд 11
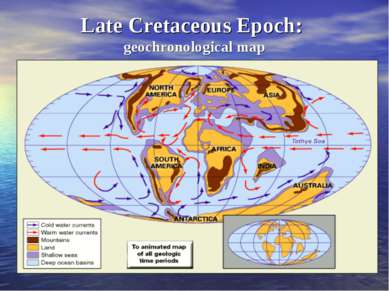
 100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Later Pangaea began to break apart. Its segments Laurasia and Gondwanaland gradually receded, resulting in the formation of the Atlantic Ocean.
100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Later Pangaea began to break apart. Its segments Laurasia and Gondwanaland gradually receded, resulting in the formation of the Atlantic Ocean.
Cлайд 12
 100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Two important groups of modern mammals evolved during the Cretaceous. Cretaceous placentals, smaller than those of present-day ones, were poised to take over the terrestrial environments as soon as the dinosaurs vanished.
100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Two important groups of modern mammals evolved during the Cretaceous. Cretaceous placentals, smaller than those of present-day ones, were poised to take over the terrestrial environments as soon as the dinosaurs vanished.
Cлайд 13
 100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Another mammal group, the marsupials, evolved during the Cretaceous as well. This group includes the native species of Australia, kangaroos, koalas, and the North American opossum.
100 million years ago Early Cretaceous Period Another mammal group, the marsupials, evolved during the Cretaceous as well. This group includes the native species of Australia, kangaroos, koalas, and the North American opossum.
Cлайд 15
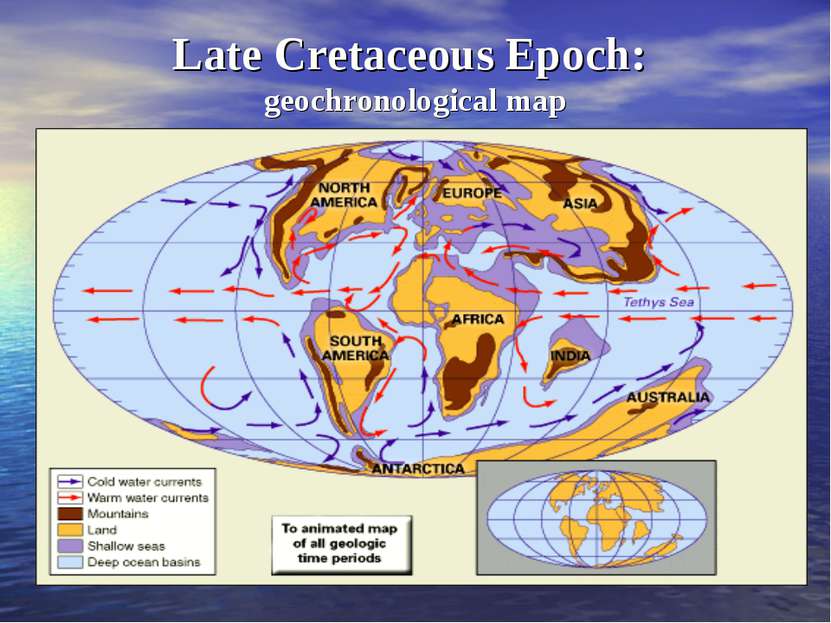
 70 million years ago The end of Cretaceous Period The Late Cretaceous record is much more complete. It is known, for instance, that during the Late Cretaceous many dinosaur types lived in relationships like the present-day terrestrial mammals.
70 million years ago The end of Cretaceous Period The Late Cretaceous record is much more complete. It is known, for instance, that during the Late Cretaceous many dinosaur types lived in relationships like the present-day terrestrial mammals.
Cлайд 16
 Diprotodon characterized by a wombat-like body the size of a large rhinoceros. massively constructed skeleton to support its imposing bulk. well developed teeth of gnawing animals. herbivorous distantly related to kangaroos and wombats. extinct marsupial mammals existed 30 - 10,000 years ago in Australia.
Diprotodon characterized by a wombat-like body the size of a large rhinoceros. massively constructed skeleton to support its imposing bulk. well developed teeth of gnawing animals. herbivorous distantly related to kangaroos and wombats. extinct marsupial mammals existed 30 - 10,000 years ago in Australia.
Cлайд 17
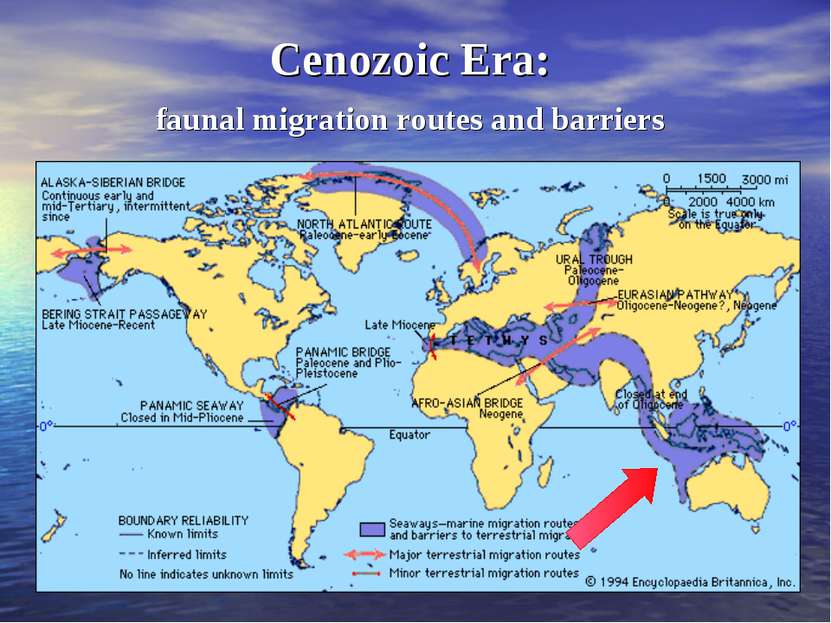
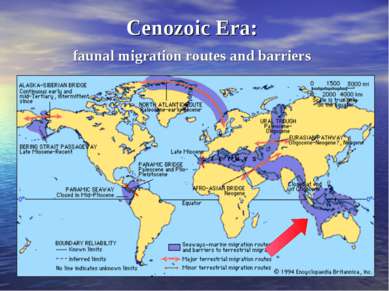
 45 million years ago The beginning of Cenozoic era By that time Australasia was isolated from all other continental masses, here marsupials evolved into many diverse forms. In South America they survived alongside placentals, forming the Neotropical mammalian fauna.
45 million years ago The beginning of Cenozoic era By that time Australasia was isolated from all other continental masses, here marsupials evolved into many diverse forms. In South America they survived alongside placentals, forming the Neotropical mammalian fauna.
Cлайд 18
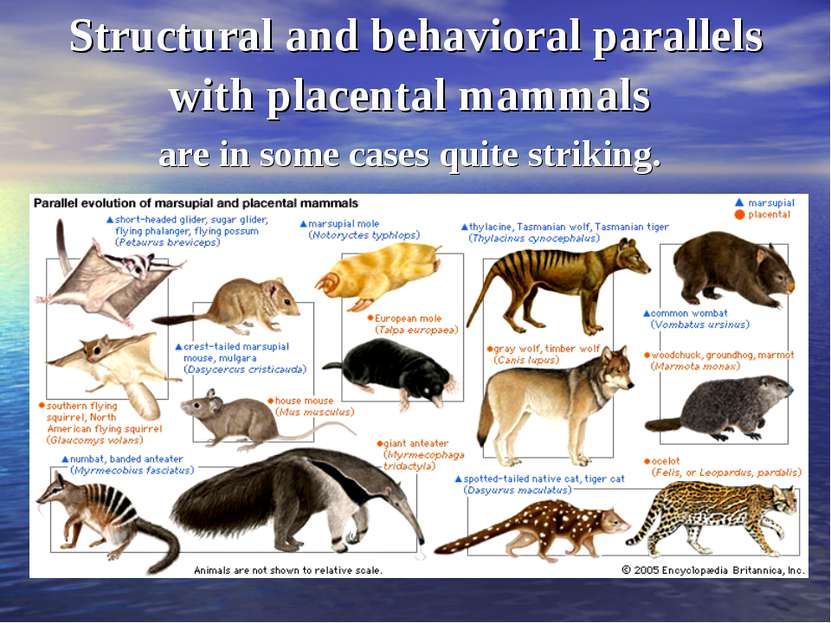
 Structural and behavioral parallels with placental mammals are in some cases quite striking.
Structural and behavioral parallels with placental mammals are in some cases quite striking.
Cлайд 19
 There are marsupials that look remarkably like moles, shrews, squirrels, mice, dogs, and hyenas.
There are marsupials that look remarkably like moles, shrews, squirrels, mice, dogs, and hyenas.
Cлайд 26
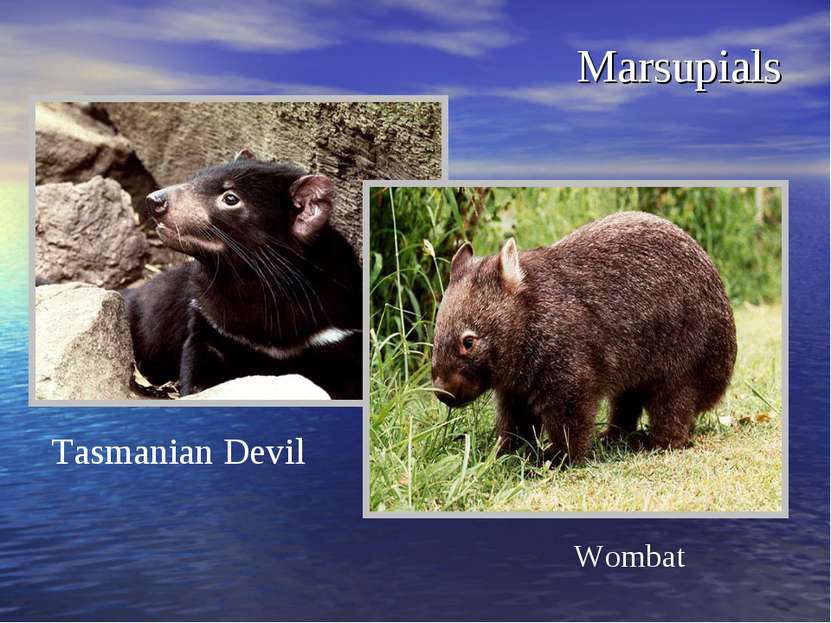
 Marsupials The niches that marsupials fill are closely associated with structure. The diets of marsupials are as varied as the niches they occupy.
Marsupials The niches that marsupials fill are closely associated with structure. The diets of marsupials are as varied as the niches they occupy.